

- #TYPES OF TRADE BLOCS FULL#
- #TYPES OF TRADE BLOCS FREE#
Non-tariff obstacles are also decreased and abolished, in addition to tariffs being removed. All trade obstacles in commodities, services, capital, and labour have been abolished.

#TYPES OF TRADE BLOCS FULL#
Common market: A 'single market' is the first major step toward full economic integration, and it occurs when member countries freely trade in all economic resources, not just tangible goods.A good example is the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Cooperation Council for Arab States of the Gulf. This means that the members can negotiate with third parties as a single bloc, such as other trading blocs or the World Trade Organization. In contrast to non-members, the customs union entails the removal of tariff barriers among members as well as acceptance of a common (unified) external tariff.
#TYPES OF TRADE BLOCS FREE#
The main distinction from a free trade zone is that members agree to treat non-member countries' trade in the same way. Trade barriers between member countries are abolished. Customs union: As in a free-trade zone, this style promotes economic cooperation.The North American Free Trade Agreement is an example (NAFTA). Member countries remove all trade barriers between themselves, but are free to set their own trade policies with non-member countries. This is the most fundamental type of economic collaboration.
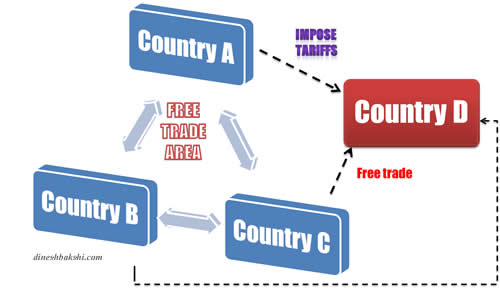
Free trade area: When two or more countries in a region agree to decrease or abolish trade barriers on all goods originating from other members, a Free Trade Area (FTA) is formed. This is frequently the first step toward forming a trading bloc. Preferential Trade Area: PTAs are formed when countries within a geographical region agree to lower or abolish tariff barriers on certain items imported from other members of the area. Preferential trading areas, free trade areas, customs unions, common markets, economic and monetary unions, and political unions are the six types of trade blocs that can be classified based on their level of economic integration. Trade blocs can be standalone accords between many states (like the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)) or part of a regional organisation (like the European Union) (such as the European Union). Advocates of global free trade are usually hostile to trading blocs, arguing that they promote regional commerce rather than global free trade. Successful trade bloc members usually share four characteristics: similar per capita GNP levels, geographic closeness, similar or compatible trading regimes, and political commitment to the regional organisation. Member states within regional blocks cooperate on economic, political, security, climatic, and other concerns impacting the region because trading is not an isolated activity. Tariffs on commodities produced by member states, import quotas, government subsidies, onerous bureaucratic import processes, and technological and other non-tariff obstacles are all used to protect against global competition. Regional trade blocs foster intra-block commerce and protect their members from global competition. Disadvantages of Regional Trading Blocs.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
